מכינה למחלקת מתמטיקה/מערכי שיעור/4: הבדלים בין גרסאות בדף
| שורה 129: | שורה 129: | ||
::<math>r=|z|</math> | ::<math>r=|z|</math> | ||
::אם <math>a>0</math> אזי <math>\varphi = arctan\Big(\frac{b}{a}\Big)</math> | |||
::<math>\varphi = arctan\Big(\frac{b}{a}\Big)</math> | ::אם <math>a<0</math>אזי <math>\varphi = arctan\Big(\frac{b}{a}\Big)+\pi</math> | ||
::אם <math>a=0</math> וגם <math>b>0</math> אזי <math>\varphi=\frac{\pi}{2}</math> | |||
::אם <math>a=0</math> וגם <math>b<0</math> אזי <math>\varphi=-\frac{\pi}{2}</math> | |||
גרסה מ־07:38, 21 ביוני 2020
פונקציות טריגונומטריות הופכיות
ניתן להגדיר פונקציה הופכית רק כאשר לכל איבר בתמונה קיים מקור יחיד. לכל פונקציה טריגונומטרית נבחר את התחום המתאים.
- [math]\displaystyle{ arcsin(x):[-1,1]\rightarrow [-\frac{\pi}{2},\frac{\pi}{2}] }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ arccos(x):[-1,1]\rightarrow [0,\pi] }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ arctan(x):(-\infty,\infty)\rightarrow [-\frac{\pi}{2},\frac{\pi}{2}] }[/math]
תרגיל: הוכח כי [math]\displaystyle{ sin\Big(arccos(x)\Big)=\sqrt{1-x^2} }[/math]
תרגילים
מצא לאילו ערכי x מתקיימים אי השיוויונים הבאים:
- [math]\displaystyle{ |cos(x)|\leq \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ sin(x^2+1)\lt 0 }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ sin(ax)\gt 0 }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ arcsin(|x-1|)\gt \frac{\pi}{4} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ sin(2x) \lt 2sin(x) }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{2}sin^2(x)-(\sqrt{2}+1)sin(x)+1 \lt 0 }[/math]
מספרים מרוכבים
נביט באוסף האיברים מהצורה
- [math]\displaystyle{ a+b\cdot i }[/math]
כאשר [math]\displaystyle{ a,b\in\mathbb{R} }[/math] והאות i הינה לצורך סימון בלבד. נקרא לאוסף זה מספרים מרוכבים.
נגדיר פעולות חיבור וכפל בין מספרים מרוכבים:
- [math]\displaystyle{ (a+b\cdot i) + (c + d\cdot i) = (a+c) + (b+d)\cdot i }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ (a+b\cdot i)(c+d\cdot i) = (ac-bd) + (bc+ad)\cdot i }[/math]
שימו לב כי [math]\displaystyle{ i^2 = -1 }[/math]
בנוסף לכל מספר מרוכב [math]\displaystyle{ z=a+bi }[/math] נגדיר את הצמוד המרוכב:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{z}=a-bi }[/math]
תרגיל חשב את [math]\displaystyle{ z\cdot \overline{z} }[/math]
פתרון [math]\displaystyle{ z\cdot \overline{z} = a^2+b^2 }[/math]
- הערה: נסמן [math]\displaystyle{ |z|=\sqrt{a^2+b^2} }[/math]
תרגיל הוכח שלכל מספר מרוכב [math]\displaystyle{ z }[/math] קיים מספר מרוכב [math]\displaystyle{ z^{-1} }[/math] כך ש [math]\displaystyle{ z\cdot z^{-1} = 1 }[/math].
פתרון: [math]\displaystyle{ z^{-1}=\frac{\overline{z}}{|z|^2} }[/math]
- הערה: באופן כללי נסמן [math]\displaystyle{ z^{-1}=\frac{1}{z} }[/math]
תרגיל חשב את הביטוי [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{5+2i}{2-3i} }[/math]
הגדרה: עבור מספר מרוכב [math]\displaystyle{ z=a+bi }[/math]
- החלק הממשי [math]\displaystyle{ Re(z)=a }[/math]
- החלק המדומה [math]\displaystyle{ Im(z)=b }[/math]
לדוגמא:
[math]\displaystyle{ Im(a-bi) = -b }[/math]
תרגיל: הוכח כי [math]\displaystyle{ |z|\geq |Re(z)| }[/math]
תרגיל: הוכח את אי-שיוויון המשולש [math]\displaystyle{ |z_1+z_2|\leq |z_1|+|z_2| }[/math]
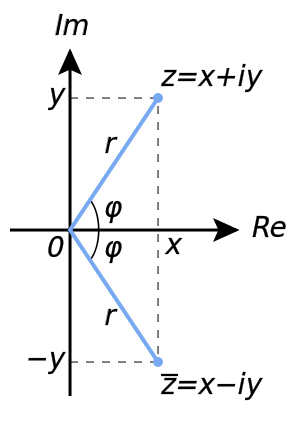
המישור המרוכב
כל מספר מרוכב [math]\displaystyle{ a+bi }[/math] מתאים לנקודה [math]\displaystyle{ (a,b) }[/math] במישור המרוכב.
ניתן לתאר את המספר המרוכב באופן יחיד באמצעות המרחק מראשית הצירים וזוית כלפי ציר האיקס.
מתקיים:
- [math]\displaystyle{ r=|z| }[/math]
- אם [math]\displaystyle{ a\gt 0 }[/math] אזי [math]\displaystyle{ \varphi = arctan\Big(\frac{b}{a}\Big) }[/math]
- אם [math]\displaystyle{ a\lt 0 }[/math]אזי [math]\displaystyle{ \varphi = arctan\Big(\frac{b}{a}\Big)+\pi }[/math]
- אם [math]\displaystyle{ a=0 }[/math] וגם [math]\displaystyle{ b\gt 0 }[/math] אזי [math]\displaystyle{ \varphi=\frac{\pi}{2} }[/math]
- אם [math]\displaystyle{ a=0 }[/math] וגם [math]\displaystyle{ b\lt 0 }[/math] אזי [math]\displaystyle{ \varphi=-\frac{\pi}{2} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ z=a+bi=r(cos(\varphi) + i\cdot sin(\varphi)) = rcis(\varphi) }[/math]
הצורה [math]\displaystyle{ rcis(\varphi) }[/math] נקראת הצורה הפולארית של המספר המרוכב, ואילו [math]\displaystyle{ a+bi }[/math] היא הצורה הקרטזית.